Inflation, like many economic
phenomena, has both pros and cons. Here are some of the potential advantages
and disadvantages of inflation:
Pros of Inflation:
Encourages Spending and
Investment: Inflation can incentivize individuals and businesses to spend
and invest rather than hold onto cash. When people expect prices to rise in the
future, they are more likely to make purchases or invest in productive assets,
stimulating economic activity.
Reduces the Real Burden of
Debt: Inflation can erode the real value of debt over time. If wages and
prices rise due to inflation, borrowers may find it easier to repay their debts
since their income is increasing in nominal terms.
Boosts Export
Competitiveness: Moderate inflation can help improve a country's export
competitiveness. As prices rise, a country's goods and services become
relatively cheaper for foreign buyers, potentially increasing export demand and
supporting economic growth.
Facilitates Price
Adjustments: Inflation allows relative price adjustments in the economy.
When the general price level rises, it provides an opportunity for businesses
to adjust their prices upward, which can help align production costs and revenues
more effectively.
Cons of Inflation:
Reduced Purchasing Power:
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. When prices rise
faster than wages, consumers can afford fewer goods and services, leading to a
decline in their standard of living.
Uncertainty and Financial
Instability: High or unpredictable inflation rates can create uncertainty
and instability in financial markets. Investors and businesses may find it
challenging to make long-term plans or decisions due to uncertain future prices.
Distorted Resource
Allocation: Inflation can distort resource allocation in the economy. When
prices rise unevenly across different sectors or regions, resources may flow
disproportionately to sectors or areas experiencing higher price increases
rather than to those with higher productivity or economic potential.
Income Redistribution:
Inflation can lead to income redistribution effects. Individuals on fixed
incomes, such as pensioners or low-wage workers, may struggle to keep up with
rising prices, while those with the ability to increase their incomes or hold
assets that appreciate in value can benefit.
Reduced Savings and
Investment: High inflation rates can discourage saving and long-term
investment. When people expect prices to rise rapidly, they may choose to spend
or invest in short-term assets rather than save for the future, potentially
hindering capital formation and long-term economic growth.
Negative Impacts on
Fixed-Income Earners: Inflation can particularly affect individuals relying
on fixed incomes, such as retirees or individuals with fixed-interest
investments. Their income may not keep pace with rising prices, leading to a
decline in their purchasing power and potentially reducing their quality of
life.
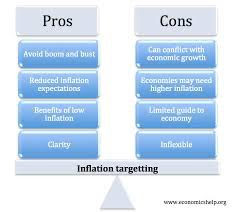



Inflation can have a significant impact on both consumers and businesses
ReplyDeletecons are much higher than pros of inflation
ReplyDeleteGood Content
ReplyDeleteAmazing Content
ReplyDelete