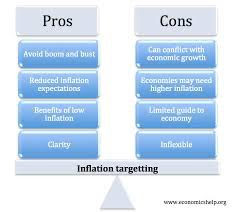
Inflation and currency exchange rates are interconnected factors that play a
significant role in shaping the global economy. Inflation, the rise in general
prices over time, can have substantial implications for currency exchange
rates, while exchange rate fluctuations can, in turn, impact inflation levels.
In this blog, we will explore the interactions between inflation and currency
exchange rates and discuss the consequences of these interactions on economies.
Inflation's Impact on Currency Exchange Rates:
1. Relative
Purchasing Power: Inflation affects a country's relative purchasing power and
competitiveness in international trade. Higher inflation rates erode the value
of a country's currency, making its goods and services relatively more
expensive compared to countries with lower inflation. This can lead to a
decrease in export demand, a deterioration in the trade balance, and a
depreciation of the currency's exchange rate.
2. Interest
Rate Differentials: Inflation differentials between countries can influence
interest rates and, consequently, currency exchange rates. Central banks may
raise interest rates in response to high inflation to control it. Higher
interest rates can attract foreign investors seeking better returns, increasing
demand for the currency and strengthening its exchange rate. Conversely, if a
country experiences lower inflation and subsequently lower interest rates,
capital outflows may occur, weakening the currency.
Currency Exchange Rates' Impact on Inflation:
1. Imported
Inflation: Exchange rate fluctuations can affect inflation levels by impacting
the prices of imported goods and raw materials. When a country's currency
depreciates, the cost of imported products rises. If the country heavily relies
on imports, higher import prices can lead to inflationary pressures.
Conversely, a strengthening currency can reduce import prices, potentially
contributing to lower inflation.
2. Inflation
Expectations: Exchange rate movements can influence inflation expectations,
which, in turn, impact actual inflation. A depreciating currency can raise inflation
expectations, as individuals anticipate higher prices for imported goods. These
expectations can lead to higher wage demands, causing a wage-price spiral and
exacerbating inflation. On the other hand, a strengthening currency may lower
inflation expectations, helping to anchor inflation and maintain price
stability.
Consequences of Inflation-Exchange Rate Interactions:
1. International
Competitiveness: Fluctuations in currency exchange rates driven by inflation
can affect a country's international competitiveness. A depreciating currency
resulting from high inflation may make exports more competitive, benefiting
domestic industries and boosting economic growth. However, if inflation remains
persistently high, the positive impact on competitiveness may be outweighed by
the negative consequences, such as reduced purchasing power for imports and
potential instability in the economy.
2. Imported
Inflation's Effects on Domestic Economy: When a country experiences inflation
due to currency depreciation and increased import prices, it can put pressure
on domestic prices. This can impact businesses' costs, consumers' purchasing
power, and overall economic stability. Imported inflation can be particularly
challenging for countries heavily dependent on imported goods and vulnerable to
global price fluctuations.
3. Monetary
Policy Challenges: Inflation-exchange rate interactions present challenges for
monetary policy. Central banks need to consider the impact of exchange rate
movements on inflation levels and vice versa. If inflationary pressures arise
from exchange rate depreciation, central banks may need to tighten monetary
policy to control inflation. However, tightening policy can also lead to
further currency depreciation, creating a delicate balancing act for policymakers.
Conclusion:
The relationship between inflation and currency exchange rates is complex
and intertwined. Inflation affects exchange rates through relative purchasing
power and interest rate differentials, while exchange rate fluctuations impact
inflation levels through imported inflation and inflation expectations. These
interactions have consequences for international competitiveness, domestic
prices, and monetary policy decisions. Understanding and managing the interplay
between inflation and currency exchange rates is crucial for maintaining price
stability, promoting economic growth, and ensuring the stability of the global
economy.